Tree Equity: We all deserve trees!
The benefits of a healthy urban forest should be available to all.

Author: Alec Sabatini / ed. Rae Tamblyn
Alec is the content writer at PlanIT Geo™, a global urban forestry consulting and tree management software firm.
In the last few years, the phrase “tree equity” has become a cornerstone in urban forestry discussions and beyond, receiving significant media attention. Tree equity encourages urban foresters, urban planners, community leaders, homeowners, and us readers to ask two vital questions:
- How equally are trees distributed within a community?
- How can we ensure everyone has access to the wonderful benefits of living near trees?

TL;DR: Trees are great for people and planet! But, city and neighborhood trees are highly concentrated in affluent, white neighborhoods and sparse in communities of color and low income. We can specifically map and plan the next generations of urban forest plantings to make trees - and their benefits - more equitable.
The Roots Of Urban Forest Inequity
How did we end up with such an uneven distribution of trees? A key factor was redlining, a discriminatory housing policy that limited home ownership and wealth creation for racial minorities. Areas with higher investment had more green space for the houses, more trees planted for neighborhood beautification, and more money invested in tree care (pruning, watering, etc.)
Studies of 37 metropolitan areas show that areas deemed “too risky” for housing loans in the 1930s still have sparse tree cover today. Although redlining ended in the 1970s and other urban planning decisions rooted in systemic racism have been phased out of development plans, trees have grown slowly. These urban forest canopies still reflect and embody past planting decisions.
The Health Implications of Tree Disparity

This isn’t just about looks; it’s a serious health concern for residents and city leaders alike. In fact, urban forests are an essential part of our neighborhood health infrastructure. Trees create a host of meaningful, measurable benefits. Collectively known as “ecosystem services,” trees and urban forests are critical to making our cities livable and sustainable. Trees provide many physical and mental health benefits. Neighborhoods with fewer trees face hotter temperatures, poorer air quality, and fewer places for recreation, leading to serious health consequences. A full list of urban forest ecosystem services runs long, but here are some of the essential benefits:
- Cooling Our Cities:
Trees are on the front lines of the battle against extreme urban heat, which as of 2022 is the number one cause of weather-related deaths in the U.S. Trees can drastically lower surface and air temperatures through shade and evapotranspiration (the exchange of water with air).
- Cleaning our Air:
Trees are sometimes known as a city's lungs, but they can also act as the liver. Urban forests can remove tons (not metaphorically, literally thousands of pounds) of air pollution every year by absorbing gasses through leaves and trapping particulates out of the air.
- Cleaning our water:
Trees improve water quality and support stormwater management through rainfall interception and infiltration (water absorbed by the soil). Stormwater infrastructure is not cheap. Cities, especially those with combined sewer systems, are turning to trees and urban forests as an effective, affordable answer to handle heavy rains as seen through the installation of rain gardens and bio-swales.
- Improving our Health:
Trees support physical health via improved air, water, and urban temperatures, but they also offer well-evidenced mental health support. Having easy access to trees or even views of trees helps reduce stress, aid recovery, and enhance our well-being. The COVID pandemic made this connection especially clear.
- Improving our Planet’s Health:
A tree pulls carbon dioxide from the air as it grows to make food and oxygen (sequestration) and stores it in roots, trunks, leaves, and soil (storage). We have a carbon issue, and urban and community trees can help offset our carbon emissions, transforming our cities from carbon problems to carbon solutions, one tree at a time.
So how do we know where to plant new trees?
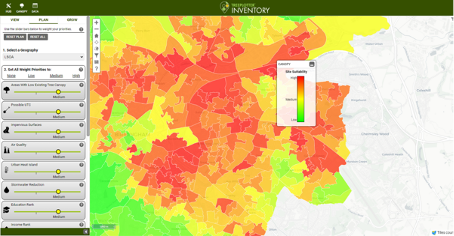
Communities use urban tree canopy (UTC) assessments. These assessments use satellite or aerial imagery to pinpoint where trees and green spaces exist. UTC assessments map existing tree canopy and layer that with other geolocated data, including race/ethnicity, income, and public health metrics. This spotlights where trees are lacking for certain groups of people and where expanding the tree canopy could have the greatest impact on living conditions.
American Forests’ Tree Equity Score is a free tool that measures tree canopy equity. It uses factors like existing tree cover, population density, income, employment, race, and urban heat islands to create a score from 0 to 100. The lower the score, the greater the need for tree investment to ensure all residents benefit from a nearby urban forest.
The tool can also be used to set targets, determine relative need, and calculate benefits of trees planted, all of which can be included in dynamic reports. “Tree Equity Score equips community leaders and urban forestry professionals with accessible and powerful data to tell stories, plan for investment, and make decisions about where trees are needed most. Paired with political will, strong and inclusive coalitions, and shared stewardship of urban forests, this information is helping to change the game for Tree Equity” said Alana Tucker, Senior Director of the Tree Equity Alliance at American Forests.
Tree planters and planners can also follow the 3-30-300 "rule" - a set of guidelines for urban forestry that aims to increase equitable access to nature and improve health and well-being. The 3-30-300 rule is based on the idea that urban forests and other urban nature can contribute to psychosocial health and well-being.
- 3 trees: Every person should be able to see at least three trees from their home, workplace, or place of learning
- 30% canopy: Neighborhoods should have a minimum of 30% tree canopy cover
- 300 meters: Everyone should live within 300 meters (about a five-minute walk) of a high-quality green space
Shifting Perceptions
Tools like the Tree Equity Score and increased access to tree canopy data are raising awareness about unbalanced tree cover. Media coverage has spread the concept, and government leaders are shifting their planning and prioritization of urban trees and equitable planning. People are starting to see urban trees as a right, not a luxury.
This shift in perspective has led to the unprecedented allocation of billions of dollars for the US Forest Service Urban and Community Forestry Program. Most of these funds will go towards tree planting and urban forest management in disadvantaged communities. Urban forest managers now use equity as a key measure in their planning. Data from equity tools helps communicate the problem, secure funding, protect existing trees, and plant new ones. Correcting these imbalances takes time, but with passionate urban forestry professionals, great data tools, and increased funding, we can make meaningful progress.
Our cities, communities, and climate are better with trees. Growing equitable urban canopies ensures that the benefits of a healthy urban forest contribute to the well-being of all people and our one planet.
Together, we can make a difference. Find a local tree planting near you! Take a #TreeSelfie and tag #TreeEquity #forestproud.
We can’t wait to dive deeper into some of these topics in the future! Let us know:
- What are you and/or your organization doing to advance tree equity?
- What questions do you have about urban forests and urban forestry?
- What stories from the sector should we cover in future blogs?
Shoot us a note: info@forestproud.org.























 Forests provide habitat for thousands of species, regulate climate, purify air and water, and support the livelihoods – and lives – of millions of people. As one of the planet’s most significant carbon sinks, forests play a pivotal role in regulating our climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2), so ensuring forests remain resilient and healthy is an essential part of climate change mitigation strategies.
Forests provide habitat for thousands of species, regulate climate, purify air and water, and support the livelihoods – and lives – of millions of people. As one of the planet’s most significant carbon sinks, forests play a pivotal role in regulating our climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2), so ensuring forests remain resilient and healthy is an essential part of climate change mitigation strategies.